Tuesday, January 11, 2011
Some Interesting facts:
Monday, January 10, 2011
application software
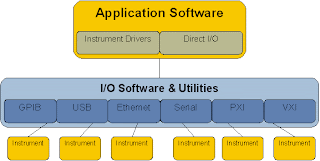
Application software, also known as an application or an "app", is computer software designed to help the user to perform singular or multiple related specific tasks. It helps to solve problems in the real world. Examples include enterprise software, accounting software, office suites, graphics software, and media players.
Application software is contrasted with system software and middleware, which manage and integrate a computer's capabilities, but typically do not directly apply them in the performance of tasks that benefit the user. A simple, if imperfect, analogy in the world of hardware would be the relationship of an electric light bulb (an application) to an electric power generation plant (a system). The power plant merely generates electricity, not itself of any real use until harnessed to an application like the electric light that performs a service that benefits the user.Application software classification
There are many types of application software:
- An application suite consists of multiple applications bundled together. They usually have related functions, features and user interfaces, and may be able to interact with each other, e.g. open each other's files. Business applications often come in suites, e.g. Microsoft Office, OpenOffice.org, and iWork, which bundle together a word processor, a spreadsheet, etc.; but suites exist for other purposes, e.g. graphics or music.
- Enterprise software addresses the needs of organization processes and data flow, often in a large distributed environment. (Examples include financial systems, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and supply-chain management software). Note that Departmental Software is a sub-type of Enterprise Software with a focus on smaller organizations or groups within a large organization. (Examples include Travel Expense Management, and IT Helpdesk)
- Enterprise infrastructure software provides common capabilities needed to support enterprise software systems. (Examples include databases, email servers, and systems for managing networks and security.)
- Information worker software addresses the needs of individuals to create and manage information, often for individual projects within a department, in contrast to enterprise management. Examples include time management, resource management, documentation tools, analytical, and collaborative. Word processors, spreadsheets, email and blog clients, personal information system, and individual media editors may aid in multiple information worker tasks.
- Content access software is software used primarily to access content without editing, but may include software that allows for content editing. Such software addresses the needs of individuals and groups to consume digital entertainment and published digital content. (Examples include Media Players, Web Browsers, Help browsers, and Games)
- Educational software is related to content access software, but has the content and/or features adapted for use in by educators or students. For example, it may deliver evaluations (tests), track progress through material, or include collaborative capabilities.
- Simulation software are computer software for simulation of physical or abstract systems for either research, training or entertainment purposes.
- Media development software addresses the needs of individuals who generate print and electronic media for others to consume, most often in a commercial or educational setting. This includes Graphic Art software, Desktop Publishing software, Multimedia Development software, HTML editors, Digital Animation editors, Digital Audio and Video composition, and many others.[2]
- Mobile applications run on hand-held devices such as mobile phones, personal digital assistants, and enterprise digital assistants : see mobile application development.
- Product engineering software is used in developing hardware and software products. This includes computer aided design (CAD), computer aided engineering (CAE), computer language editing and compiling tools, Integrated Development Environments, and Application Programmer Interfaces. YUH ZEIT * A command-driven interface is one in which you type in commands to make the computer do something. You have to know the commands and what they do and they have to be typed correctly. DOS and Unix are examples of command-driven interfaces.
- A graphical user interface (GUI) is one in which you select command choices from various menus, buttons and icons using a mouse. It is a user-friendly interface. The Windows and Mac OS are both graphical user interfaces
Regarding posts !
Hope you understood me friends hoping to learn many new things not just only related to subject but about everything..
Thanks :)
Sabir
Sunday, January 9, 2011
intel i7 processor
2nd Generation Intel® Core™ i7 Processor
The Intel® Core™ i7 processor delivers best-in-class performance for the most demanding applications. This quad-core processor features 8-way multitasking capability and additional L3 cache. With adaptive performance and built-in visual capabilities this 2nd generation processor brings more intelligence to your PC.
2nd generation Intel® Core™ i7 processors feature Intel® Turbo Boost Technology 2.0◊ and Intel® Hyper-Threading TechnologyΔ, enabling required security applications and protocols to run efficiently in the background without compromising productivity.
Today's more visually sophisticated communication needs will be met with Intel® HD Graphics 2000 Technology, integrated into 2nd generation Intel Core processors. This eliminates the need for a discrete graphics card, reducing power consumption and system cost.
FEATURES AND BENEFITS
With 2nd generation Intel Core i7 processors, you get the following features built in:
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology 2.0◊ dynamically increases the processor frequency as needed by taking advantage of thermal and power headroom when operating below specified limits.
Intel® HT TechnologyΔ allows each core of your processor to work on two tasks at the same time.
Intel® Smart Cache is dynamically allocated to each processor core based on workload, which significantly reduces latency and improves performance.
Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions add hardware acceleration to AES algorithms and speeds up the execution of AES applications.
Microprocessor-Simplified Model

Microprocessor: Simplified Model
Arithmetic & Logic Unit (ALU)
The part of the central processing unit that deals with operations such as addition, subtraction and multiplication of integers and boolean operations. It receives control signals from the control unit telling it to carry out these operations.
Control Unit (CU)
It controls the movement of instructions in and out of the processor, and also controls the operation of the ALU. It consists of a decoder, control logic circuits, and a clock to ensure everything happens at the correct time. It is also responsible for performing the instruction execution cycle.
Register Array
It is a small amount of internal memory that is used for the quick storage and retrieval of data and instructions. All processors include some common registers used for specific functions, namely the program counter, instruction register, accumulator, memory address register and stack pointer.
System Bus
It is comprised of the control bus, data bus and address bus. It is used for connections between the processor, memory and peripherals, and transfer of data between the various parts.
Memory
The memory is not an actual part of the CPU itself, and is instead housed elsewhere on the motherboard. However, it is here that the program being executed is stored, and as such is a crucial part of the overall structure involved in program execution.